Dissociation equilibrium with Cobra4
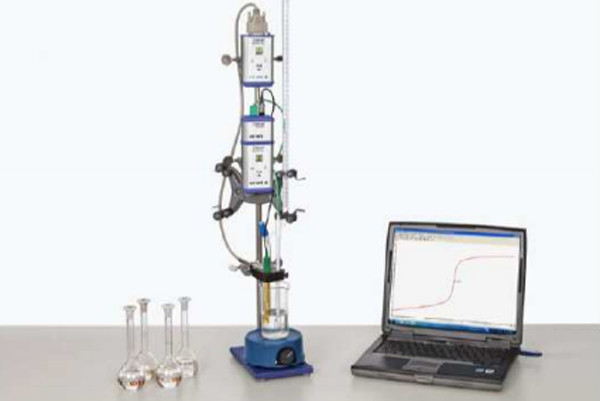
Carboxylic acids are potential electrolytes which exist in a weakly dissociated condition in aqueous solutions. The location of the dissociation equilibrium is quantitatively described by the Ka or pKa value which can be determined with potentiometric measurements.
- Simplified implementation: all pre-settings already prepared
- Drop counter optimizes the experimental procedure
USB charger for Cobra4 Mobile-Link 2 and Wireless/USB-Link
Cobra4 Wireless/USB-Link incl. USB cable
Cobra4 Sensor-Unit Chemistry
Cobra4 Sensor-Unit Drop Counter
Holder for sensors with support rod
Immersion probe NiCr-Ni, teflon, 300 °C
N-butyric acid 100
Monochloroacetic acid 100 g
Lactic acid 100
Buffer solution, pH 4.62 1000
Buffer solution, pH 9 1000
Water, distilled 5 l
Acetic acid 99…100%, pure 1
Propionic acid, 500
Microspoon, steel
Wash bottle, plastic, 500 ml
Magnetic stirrer without heating, 3 ltr., 230 V
Beaker, tall form, 150 ml
Burette, lateral stopcock, Schellbach, 25 ml
Volumetric flask 100 ml, IGJ12/21
Volumetric pipette, 5 ml
Pipette dish
Pasteur pipettes, 250 pcs
Pipettor
Retort stand, h = 750 mm
Right angle boss-head clamp
Burette clamp, roller mount., 2 pl.
Rubber stopper,d=18/14mm, 1 hole
Rubber caps, 10 pcs
Beaker, 50 ml, high-form
Beaker, 250 ml, high-form
pH-electrode, plastic body, gel, BNC
Magnetic stirring bar 15 mm, cylindrical
Caustic soda sol.,0.1M 1000
curricuLAB measureLAB
- Measure the alteration of the pH value during a titration of approximately 0.1 molar aqueous solutions of formic acid, acetic acid, monochloroacetic acid, propionic acid, butyric acid and lactic acid with a 0.1 molar sodium hydroxide solution at constant temperature using Cobra4 system.
- From the neutralisation curves read the pKa values of the acids and compare them.
- True and potential electrolytes
- Strong and weak acids
- Law of mass action
- Henderson-Hasselbalch equation
- Dissociation constant and pKa value
- Substituent effects
- Potentiometry
