Peltier heat pump
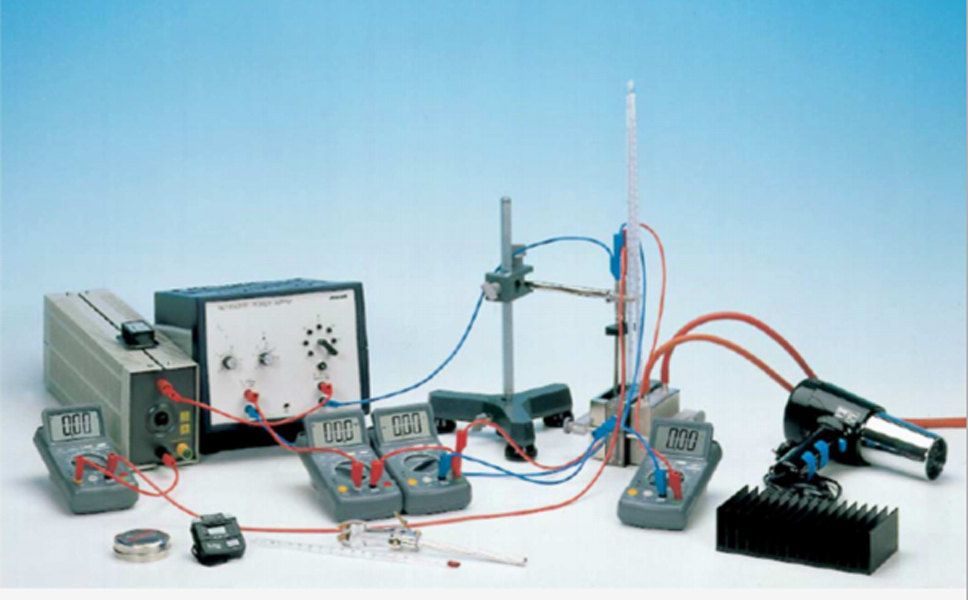
The (cooling capacity) heating capacity and efficiency rating of a Peltier heat pump are determined under different operating conditions
- Open design allows to fully understand function and applications
- Individual instruments for distinct functions (no “black box”)
- Key products of the experiment setup can also be used for investigating the Seebeck effect
Universal clamp
Thermometer -10…+50 °C
Lab thermometer,-10..+110 °C
Rubber tubing, i.d. 6 mm
Tripod base PHYWE
Support rod, stainless steel, l = 250 mm, d = 10 mm
Stopwatch, digital, 1/100 s
Heat conductive paste,50 g
Hot/cold air blower, 1800 W
Thermogenerator with 2 water baths
Flow-through heat exchanger
Air cooler
Heating coil with sockets
Distributor
Rheostat, 33 Ohm , 3.1A
Digital multimeter 2005
Connecting plug, 2 pcs.
Connecting cord, 32 A, 250 mm, red
Connecting cord, 32 A, 500 mm, red
Connecting cord, 32 A, 500 mm, blue
Connecting cord, 32 A, 750 mm, red
Connecting cord, 32 A, 750 mm, blue
PHYWE power supply, universal DC: 0…18 V, 0…5 A / AC: 2/4/6/8/10/12/15 V, 5 A
Right angle clamp expert
- To determine the cooling capacity Pc of the pump as a function of the current and to calculate the efficiency rating hc at maximum output.
- To determine the heating capacity Pw of the pump and its efficiency rating hw at constant current and constant temperature on the cold side.
- To determine Pw, ηw and Pc , ηc from the relationship between temperature and time on the hot and cold sides.
- To investigate the temperature behaviour when the pump is used for cooling, with the hot side air-cooled.
- Peltier effect
- Heat pipe
- Thermoelectric e. m. f.
- Peltier coefficient
- Cooling capacity
- Heating capacity
- Efficiency rating
- Thomson coefficient
- Seebeck coefficient
- Thomson equations
- Heat conduction
- Convection
- Forced cooling
- Joule effect
